An estimated 90,000 Americans are diagnosed with Parkinson's disease every year. Even though there is no cure for Parkinson's disease right now, there are many treatments that can help with symptoms and improve quality of life.
Taking small amounts of Delta 9 THC has been gaining attention as a viable therapy option to treat Parkinson’s in recent years.

Microdosing is the practice of ingesting small quantities of cannabis to achieve therapeutic benefits and treat anything from stress and anxiety to depression to insomnia, glaucoma, and inflammation.
Our edibles are the best, safest, and most reliable way to ingest small amounts of Delta 9, CBD, and other cannabis extracts. Don’t believe us? Shop our low-dose THC gummies and see for yourself.
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder that affects the motor system. Parts of the central nervous system gradually become damaged, resulting in motor and non-motor symptoms such as tremors, fatigue, and impaired cognition.
Most patients start to develop PD symptoms after the age of 50. According to study reviews, Parkinson's disease is statistically twice as common in men than in women.
The most common symptoms of PD are resting tremor, slow movement, and muscle stiffness. People with Parkinson’s may develop a wide range of other physical, psychological, and cognitive problems.
- Motor symptoms
- Tremors, uncontrollable shaking
- Rigidity: stiffness and resistance in the muscles
- Bradykinesia: sluggish movement and difficulty initiating and terminating movement
- Instability of posture and balance: trouble maintaining coordination
- Paresthesia: tingling and numbness
2. Non-motor symptoms
- Sleep disruption, daytime sleepiness, and REM behavior disorder
- Autonomic dysfunction (dysautonomia)
- Changes in perception: impaired or full loss of sense of smell (anosmia), disturbed vision
- Gastrointestinal problems like constipation
- Fatigue
- Urinary incontinence
- Orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure upon standing)
- Excessive sweating and oily skin
3. Cognitive symptoms
- Cognitive flexibility
- Problems with planning and memory loss
- Impaired perception and estimation of time
- Slowed cognitive processing speed
People with PD often experience significant mental and mood disorders. Psychosis affects anywhere from 26% to 83% of patients. Patients with PD frequently struggle with conditions like anxiety, apathy, and clinical depression, with a high prevalence of suicidal thoughts.
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease?
The cause of Parkinson’s disease is largely unknown. A number of risk factors and causes have been proposed, but none have been proven yet.
Parkinson’s disease onset is positively correlated with pesticide exposure and negatively correlated with smoking. Other researchers propose a possible association between Parkinson's disease and Helicobacter pylori infection, which might inhibit the absorption of certain PD medications like levodopa.
Genetic factors seem to increase the risk of developing the disease, which is present in some 5–10% of PD patients. Research in Parkinson’s disease genetics has shown a compelling number of individuals with PD who have a first-degree relative with the disease.
As a neurodegenerative disorder, Parkinson’s is mainly caused by a loss of nerve cells in the substantia nigra, a brain region critical for the production of dopamine. Among other things, dopamine regulates body movement. Parkinson’s symptoms may be caused directly by a decreased amount of dopamine in the brain.
The Impact of Dopamine Deficiency on Parkinson’s
Dopamine is an important neurotransmitter that affects a wide range of physical functions and brain activities. Also known as the “happy hormone,” dopamine regulates sleep, mood, control of nausea and vomiting, pain processing, and movement.
The loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra could be a defining sign of Parkinson’s disease. The main purpose of dopamine, as a neurotransmitter, is to carry messages between nerve cells in the basal ganglia, a group of brain structures (including the substantia nigra) that send and receive signals that control movement. When dopamine levels are low, the communication between brain cells is disrupted, and control over movement becomes impaired or completely lost. Reduced levels of dopamine impair the functioning of the basal ganglia, leading to tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia.
The happy hormone is involved in keeping us elevated and happy. Low levels of dopamine in the brain might leave a person feeling sad and lacking motivation and focus. Dopamine deficiency can lead to clinical depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment.
Some Parkinson’s treatments focus on restoring the balance of dopamine in the brain by improving the signaling between neurons in the basal ganglia. Cannabis users report positive benefits of THC microdosing in treating anxiety, depression, and other mental conditions caused by dopamine deficiency.
Cannabis is frequently microdosed to boost dopamine levels, which is good both for mental health and for treating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Our low-THC Bliss gummies are a great way to elevate your depleted levels of dopamine. They contain equal amounts of THC and CBD that bring out a mild euphoria while making you feel relaxed. While these delicious vegan-friendly edibles will not cure the disease, low-dose THC can help with the symptoms of Parkinson’s and other movement disorders.
Do you want to learn more about cannabidiol? Our extensive guide to CBD might be just what you’re looking for.
Effects of Low-Dose THC on Parkinson’s
Legalization of cannabis has allowed many patients to use it as a treatment option for both mental and physical ailments. People turn to cannabis to relieve anxiety, reduce pain and inflammation, promote sleep, and even treat glaucoma and ADHD.
Tetrahydrocannabinol has powerful analgesic, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant properties. Low doses of THC can soothe pain signals, lower stress and anxiety, and treat conditions that involve seizures, tremors, and muscle stiffness.
Do you need a quick refresher course on tetrahydrocannabinol? Take a look at our holistic guide to THC.
To understand how THC affects our body, we must first understand how it delivers contrasting results at different doses, a phenomenon known as the biphasic effect.
Our edibles contain low, safe amounts of Delta 9 THC and other cannabis compounds that don’t cause adverse effects. The standard THC dose in our edibles is between 5 and 10 mg, while some of our hemp products contain ultra-low doses of THC. Try our Sleep Plus gummies, a natural and irreplaceable sleep aid that contains only 2 mg of THC.
Read more about how microdosing cannabis can promote healthy sleep.
How Parkinson’s Affects the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex network of signals and receptors found throughout the body that regulate a range of physiological functions such as pain, mood, appetite, sleep, and motor control.
CB1 and CB2 receptors, the two major cannabinoid receptors, are activated by both endocannabinoids produced by our bodies and phytocannabinoids extracted from the cannabis plant. While CB1 receptors are located mainly in the brain and central nervous system, CB2 receptors are present largely in the immune system and peripheral tissues, where they help control inflammation and immunological function.
The functioning of the endocannabinoid system seems to be related to many medical conditions, including movement disorders. The loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain creates a disbalance in the ECS. Through cannabinoid receptors, the ECS regulates essential systems affected by Parkinson’s disease, such as motor control, mood, and sleep.
CB1 and CB2 receptors are found in parts of the brain affected by Parkinson’s, implying that targeting these receptors may have therapeutic potential in treating the disease. Remember the substantia nigra, the brain area that produces dopamine? According to Parkinson’s research, the substantia nigra seems to aid motor control, as it contains the highest density of CB1 receptors in the brain.
Further research shows that activation of CB1 receptors protects against depressive-like behavior and levodopa-induced dyskinesia (involuntary, erratic movements).
Phytocannabinoids like THC and cannabidiol (CBD) mimic the functions of endogenous endocannabinoids, binding to cannabinoid receptors and activating the ECS. Phytocannabinoids may even have more pronounced therapeutic benefits for our ECS, especially at low doses.
Let’s take a closer look at the mechanisms of microdoses of THC in treating Parkinson’s disease.
THC’s Role in Treating Parkinson’s
Delta 9 is the most common THC variant. At low doses, THC exerts beneficial effects on the body, with little to no psychoactivity. Commonly referred to as THC, Delta 9 is known for generating feelings of euphoria and relaxation, stimulating appetite, relieving pain, and so much more.
THC is a cannabinoid receptor agonist, which means it binds directly to CB1 receptors. This interaction allows THC to:
- Relieve pain
- Lower anxiety and depression
- Produce antiemetic effects: THC is frequently used in treating symptoms of chemotherapy, specifically nausea and vomiting
- Produce anticonvulsant effects: low THC doses can prevent and treat epilepsy-related seizures
A 2022 systematic review found a potential positive effect of consuming cannabis to alleviate PD-related symptoms like tremor, chronic pain, anxiety, and poor sleep quality.
A study review of the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids indicates that:
- Cannabis use is associated with decreased pain and spasticity in people with multiple sclerosis.
- Chronic low doses of CBD and THC decreases pain and spasticity and improves appetite in ALS patients.
- Low amounts of cannabis may improve food intake, quality of sleep, and diminish agitation and aggression in late stage Alzheimer’s disease. (Find out more about how microdosing THC and CBD improves symptoms of dementia.)
- THC can lower tremor, rigidity, and chronic pain in people living with Parkinson’s.
- THC has also demonstrated an improvement in activity and hand-eye coordination in animal models of Parkinson’s.
We’ve already established that dopamine has an important role in Parkinson’s disease. It maintains normal communication between nerve cells in the basal ganglia and prevents tremors and muscle rigidity. When THC is consumed, levels of dopamine rise, producing feelings of pleasure and euphoria.
In addition, THC has potent anti-inflammatory properties, which help protect the dopaminergic neurons that PD tends to impair or completely destroy.
THC’s potential to stimulate dopamine release, reduce inflammation, treat chronic pain associated with tremors and rigidity, and improve mood makes it an intriguing treatment option for Parkinson’s. To maximize its therapeutic advantages, THC should be consumed at low doses.
There’s no better way to boost the happy hormone and bring forth pure relaxation other than our Relax Plus gummies. Containing only five milligrams of THC and 25 mg of CBD, these fresh watermelon edibles produce a light buzz in the most delicious way.
Is CBD Better than THC for Parkinson’s?
Unlike THC, CBD does not produce a high. It is well-known for its soothing and relaxing properties that help treat anxiety, insomnia, chronic pain, inflammation, and many other ailments.
CBD does not bind significantly to either of the cannabinoid receptors. Instead, it impacts the ECS by regulating how THC interacts with CB1 and CB2 receptors. CBD reduces the likelihood of adverse effects from THC and maximizes its therapeutic potential.
CBD has potent neuroprotective effects. A review of clinical and preclinical studies suggests that it could treat movement disorders and other conditions linked to neurodegeneration by improving motor function.
Other research demonstrates the powerful effects of cannabidiol on sleep. People with Parkinson’s disease often struggle with REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD). This condition causes the patients to act out their dreams while asleep, which normally doesn’t happen in healthy individuals. In a 2014 case report, four patients suffering from RBD were treated with CBD and experienced a prompt and significant decrease in the frequency of their RBD-related symptoms.
The positive effect of CBD on stress and anxiety draws many patients in the Parkinson’s community to turn to cannabidiol for relief. CBD has been suggested as a promising method of treating psychosis in Parkinson’s disease. Participants in one pilot study were given flexible doses of CBD for 4 weeks, in addition to their usual therapy. The results showed that CBD significantly decreased psychotic symptoms without aggravating the participants' motor function.
Just like THC, CBD has significant anti-inflammatory potential that helps treat a wide range of chronic inflammatory conditions. In fact, CBD and THC share many effects and health benefits. In terms of the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, the best results are achieved when THC and CBD are taken together.
Take a closer look at the complementary differences between THC and CBD.
Product QUIZ
Need help deciding what product is best for you? Take our quiz, just three questions until your perfect match!
The Entourage Effect on PD
The entourage effect is a theory that describes the increased therapeutic effects when CBD and THC are combined. THC and CBD together have been found to be more beneficial than either ingredient alone in treating symptoms of many medical conditions, including Parkinson's disease symptoms.
THC soothes the pain receptors and lowers inflammation, while CBD’s neuroprotective properties help alleviate some of the symptoms of PD like tremor and psychosis. Also, CBD seems to make THC work better by making it take longer for the body to break down THC, so the effects last longer.
Full spectrum CBD contains two major cannabinoids (THC and CBD) as well as other minor compounds, terpenes, and flavonoids. Cannabis research suggests that the combination of extracts in full spectrum CBD offers more medicinal benefits than broad spectrum CBD. (In broad spectrum hemp extracts, there are no traces of Delta 9 THC.)
Shop our delightful full spectrum gummies and witness the powerful synergy of Delta 9 and CBD working together to alleviate symptoms of PD and many other conditions.
If you’re thinking about microdosing cannabis without THC, try our broad spectrum gummies. They may not be as efficient in relieving tremors and improving sleep as their THC-rich counterparts, but they are equally delicious!
Best Edibles for Parkinson’s Disease
For the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, low doses of THC seem to provide the greatest relief. Low-dose edibles with 2.5–5 mg of THC and an equal or greater content of CBD seem to alleviate motor and non-motor symptoms, improve sleep, and increase dopamine.
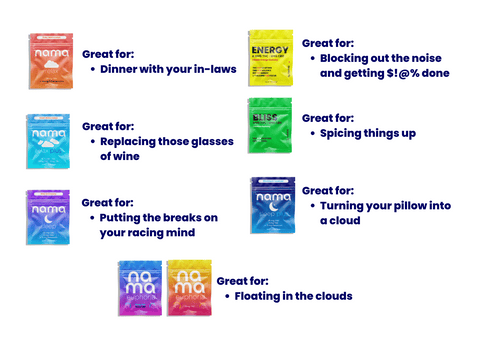
- Lack of sleep, REM sleep behavior disorder, and other sleep issues are something people with PD face nearly every day. Our Sleep Plus gummies are the ultimate sleep aid. This unique blend of 2 mg of THC, 25 mg of CBD, and 3 mg of melatonin will provide PD patients with a soothing eight-hour sleep they truly deserve.
- If you’re new to microdosing—or new to cannabis altogether—our Relax Plus gummies offer the sweetest introduction to the world of low-dose THC edibles. 5 mg of THC combined with 25 mg of CBD provide deep relaxation, muscle tension relief, relief from tremors and stiffness, and much needed pain alleviation.
- Our Energy Delta 9 gummies combine only 2.5 mg of THC with 5 mg of CBD to keep your brain up and running. Infused with blood orange, these exotic fruity chews are the perfect way to protect your little gray cells and keep those dopamine-releasing parts of the brain nice and smooth.
- Did someone say dopamine? Meet our phenomenal Bliss gummies with an equal concentration of THC and CBD (5 mg per yummy gummy). They’re excellent for that sweet dopamine release that provides a relief from stress, anxiety, and depression. Bliss has never tasted better.
We often combine our sleep gummies with melatonin for a greater therapeutic effect. Learn more about what melatonin is and how it promotes healthy sleep.
Parkinson’s Disease FAQ
Can you prevent PD?
While there is no proven way to completely prevent it, some lifestyle habits may help reduce the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
Regular physical activity has been suggested as a viable technique to minimize the risk of Parkinson’s and promote overall health. Aerobics promote brain health and lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s.
As a bonus, physical activity is a great way to boost and maintain dopamine levels in the brain. In particular, aerobic exercise appears to enhance blood flow and oxygenation to the brain.
According to a research article, regular coffee consumption might have a preventive impact against Parkinson's, although the exact link between caffeine and PD is still unknown. Other research suggests a similar association between PD and tobacco. Clinical studies on the possible environmental-genetic causes of PD found that non-smokers seem to be more susceptible to developing PD symptoms than smokers.
No matter how smoking and caffeine help prevent Parkinson's disease (PD), researchers point out the bad effects of too much smoking and caffeine on health. It is not recommended to take up smoking or increase caffeine consumption to avoid Parkinson’s disease.
As a great way to promote brain health, mental health, and the homeostasis of your entire body, we recommend taking up microdosing. With our delicious, organic edibles, you can enjoy a variety of flavors and cannabinoid ratios.
Have you heard of our strawberry-infused Euphoria gummies? Ten milligrams of Delta 9 THC will grant the most enjoyable euphoric kick, while an equal concentration of CBD will take away all the stress.
Can you take CBD oil with carbidopa/levodopa?
It is perfectly safe to take CBD oil with the medications for Parkinson’s disease: carbidopa and levodopa. Most research on cannabis and Parkinson’s considers low doses of CBD and THC a valuable adjunctive medicine for the treatment of Parkinson's and suggests that cannabis may even slow the progression of the disease.
While CBD oil is a good alternative to smoking cannabis, nothing beats microdosing edibles. Now is the right time to order our CBD gummies and enjoy the wide range of therapeutic benefits of CBD.
Remember that CBD does not have psychoactive properties and cannot produce euphoria. For that sweet euphoric kick, shop the most amazing Delta 9 edibles and experience the ultimate canna-bliss!
How to use CBD oil for Parkinson’s?
When used correctly, CBD oil is a safe and effective strategy to alleviate symptoms of Parkinson’s and enhance overall quality of life.
Studies on medical marijuana and Parkinson's disease frequently use dosages between 150 and 400 milligrams of CBD. While this amount may have positive effects on experienced cannabis users, beginners diagnosed with PD should start their microdosing journey with a much lower dosage and gradually increase it as they feel comfortable.
A typical starting dose is 5–10 mg, taken once or twice a day, orally or sublingually. For first-time users, it may go even lower, between 2 and 3 mg. It is important to be consistent and patient with dosing and to allow the CBD to build up in your system.
Another crucial thing is the quality of the CBD oil. Always buy from a trustworthy supplier and check with your healthcare practitioner before beginning any new treatment program.
CBD oil makes a great alternative to the unhealthy practice of smoking cannabis, but it doesn’t come without disadvantages. Precise dosing with oils can be challenging. Typically, one drop equals one milligram of the liquid, but it is hard to determine how much CBD is contained in one drop of oil.
We have a better, tastier, and more reliable solution. Why drop bland oils on your tongue when you can chew real fruit?
Meet our CBD sleep edibles! Premium CBD extracted from the hemp plant (not marijuana) and infused into the most delectable microdosing edibles to fight insomnia like there’s no mañana. Some of the products contain small amounts of Delta 9 THC, while others are made with pure CBN. All of our hemp products are made with the highest quality ingredients and real fruit (no artificial flavors added).
Are you curious to learn more about CBN? Here’s our in-depth look at cannabinol.
Can THC prevent dementia?
Dementia patients have reported that medical cannabis helps with pain relief, increased appetite, and an overall sense of calm. Elderly patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia have benefited from THC-rich cannabis extracts, citing a reduction in medication consumption, weight gain, and sleep improvement.
Dementia researchers often focus on the most common change in behavior in patients with Alzheimer’s and dementia: a decrease in agitation and aggression. Existing anti-aggression medications come with harmful side effects, but cannabinoids interact with the body in a gentler way.
While many people are concerned about the negative sides of using cannabis, microdosing THC comes with no adverse effects. Low doses of THC, CBD, and other similarly beneficial cannabis compounds seem to promote brain health, improve memory, and slow the progression of neurological conditions.
Is THC legal?
Delta 9 THC is federally legal, provided the product is compliant with the 2018 Farm Bill.
For Farm Bill compliance, a product must meet the following criteria:
- The Delta 9 THC must come from hemp, not marijuana.
- The THC product must not contain more than 0.3% of Delta 9 THC by dry weight.
Despite federal legality, each state can determine which hemp-derived products are legal in that state. Our edibles are federally legal and available for shipping across 48 states, with two US states making hemp-derived products illegal (we’re looking at you, Idaho and Kansas).
Before you decide on your purchase, make sure to check whether your state is Delta 9-friendly.
Are you interested in shopping for the best edibles on this side of the galaxy but not sure where to look? We’ve got you covered. Check out this extensive guide to where to buy Delta 9 gummies in the US.
Why is it called Parkinson’s disease?
Parkinson’s disease is one of the most prevalent neurodegenerative diseases in the world, yet many people don’t know the story behind its name.
This condition was named after the English physician, James Parkinson, who first described the shaking palsy in 1817. He wrote a comprehensive description of the disease, which helped doctors and researchers identify it as the condition we today know as Parkinson’s.
The term itself was coined much later, in 1865, by a French neurologist, Jean-Martin Charcot.
Resources
“Parkinson’s Disease in Women and Men: What’s the Difference? - PubMed.” PubMed, 1 Jan. 2019, https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-191683.
“Pesticide Exposure and Risk for Parkinson’s Disease - PubMed.” PubMed, 1 Aug. 2006, https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20904.
Çamcı, Gülşah, and Sıdıka Oğuz. “Association Between Parkinson’s Disease and Helicobacter Pylori.” PubMed Central (PMC), 26 Feb. 2016, https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2016.12.2.147.
“Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease - PubMed.” PubMed, 1 Aug. 2017, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1686-y.
Lesage, Suzanne, and Alexis Brice. “Parkinson’s Disease: From Monogenic Forms to Genetic Susceptibility Factors.” OUP Academic, 15 Apr. 2009, https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddp012.
“The Therapeutic Role of Cannabinoid Receptors and Its Agonists or Antagonists in Parkinson’s Disease - PubMed.” PubMed, 10 Jan. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109745.
Patel, Rikinkumar S., et al. “Pros and Cons of Marijuana in Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease.” PubMed Central (PMC), 3 June 2019, https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.4813.
“Effects of Cannabis in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis - PubMed.” PubMed, 1 Jan. 2022, https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-212923.
Suryadevara, Uma, et al. “Pros and Cons of Medical Cannabis Use by People With Chronic Brain Disorders.” PubMed Central (PMC), 1 Aug. 2017, https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X14666161101095325.
Peres, Fernanda F., et al. “Cannabidiol as a Promising Strategy to Treat and Prevent Movement Disorders?” Frontiers, 24 Apr. 2018, https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00482.
Chagas, M. H. N., et al. “Cannabidiol Can Improve Complex Sleep-related Behaviours Associated With Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behaviour Disorder in Parkinson’s Disease Patients: A Case Series.” Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, vol. 39, no. 5, Hindawi Limited, May 2014, pp. 564–66. Crossref, https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpt.12179.
Zuardi, AW, et al. “Cannabidiol for the Treatment of Psychosis in Parkinson’s Disease.” Journal of Psychopharmacology, vol. 23, no. 8, SAGE Publications, Sept. 2008, pp. 979–83. Crossref, https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881108096519.
Costa, João, et al. “Caffeine Exposure and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studiess - IOS Press.” Caffeine Exposure and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studiess - IOS Press, 14 Apr. 2010, https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2010-091525.
Tsuboi, Yoshio. “Environmental-Genetic Interactions in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease.” PubMed Central (PMC), 17 Sept. 2012, https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2012.21.3.123.
Rieder, Carlos R. “Cannabidiol in Parkinson’s Disease.” PubMed Central (PMC), 24 Mar. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-4446-2019-0810.
nama CBD FDA & Legal Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. Our products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. They are not a replacement for prescription medications and have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice or any statements of the status of any laws. Any information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only, and are not intended to be relied upon for any purpose.
Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter including decisions on what products are, or are not, legal to sell, possess, or consume. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from their own counsel in the relevant jurisdiction.
Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or accurate for your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser, and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
More From the nama Family
Small batch edibles crafted for different times of the day and experiences.
More articles
About
Learn
Join us on this journey

© Copyright 2025 nama Products LLC. All Rights Reserved.
†These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. All information presented here is not meant as a substitute for or alternative to information from health care practitioners. Please consult your health care professional about potential interactions or other possible complications before using any product.
††The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice or any statements of the status of any laws. Any information, content, and materials available on this site are for general entertainment purposes only, and are not intended to be relied upon for any purpose.
123 John Doe Street
Your Town, YT 12345
Store Hours
Sun: Closed
Mon-Fri: 9:00 - 17:00
Sat: 10:00 - 13:00
What to expect at pickup
Closed
Closing at 5pm
Closing at 5pm
Closing at 5pm
Closing at 5pm
Closing at 5pm
Closing at 1pm

![Buzz Packs™ [THC and CBD Powder Drink Mix]](http://www.namacbd.com/cdn/shop/files/nama_buzz_packs_thc_drink_pack_white_background.png?v=1741884660&width=480)
![Buzz Packs™ [THC and CBD Powder Drink Mix]](http://www.namacbd.com/cdn/shop/files/Buzz_Packs_Label.png?v=1741884660&width=480)






















![Buzz Drops™ [THC Drink Drops]](http://www.namacbd.com/cdn/shop/files/nama_thc_buzz_drops.png?v=1711412866&width=480)
![Buzz Drops™ [THC Drink Drops]](http://www.namacbd.com/cdn/shop/files/buzz-drop-wine-comparison.png?v=1736882023&width=480)





Comments (0)
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!